Describe How the Sun Changes Over Its Lifetime
_____ _____ _____ Select normal speed and click the play button below the information panel to start the evolution of the lifecycle of our Sun and observe the changes in its size. When the Sun is north of the equator then it will rise at an azimuth north of exact east and when it is south of equator it will rize at an azimuth south of exact east.

5 Things Your Marriage Needs Every Day Quotes Marriage Quotes Inspirational Quotes
Up to 24 cash back 3.

. Stars lose mass gradually by converting hydrogen into helium and heavier elements. In this section we describe the huge changes that occur in the Suns extensive interior and atmosphere and the dynamic and violent eruptions that occur daily in its outer layers. The Sun like most stars in the Universe is on the main sequence stage of its life during which nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium.
They can also lose mass through winds blowing off their surface and at dramatic moments in their lives. Yet this atmosphere didnt last for very long because the solar wind from the sun blew it away. To do so all it needs is a.
Describe what will happen to our Sun as it evolves into a White Dwarf. The Sun reaches its highest point at a variety of times as the seasons change not merely at noon every day. Click the play button below the HertzsprungRussell diagram to show the Suns evolution.
The planet is generally thought of as having three distinct atmospheres over the course of its lifetime. The same as the Sun. This phase in a stars life is called the Main Sequence and a star spends a major part of its life in this phase.
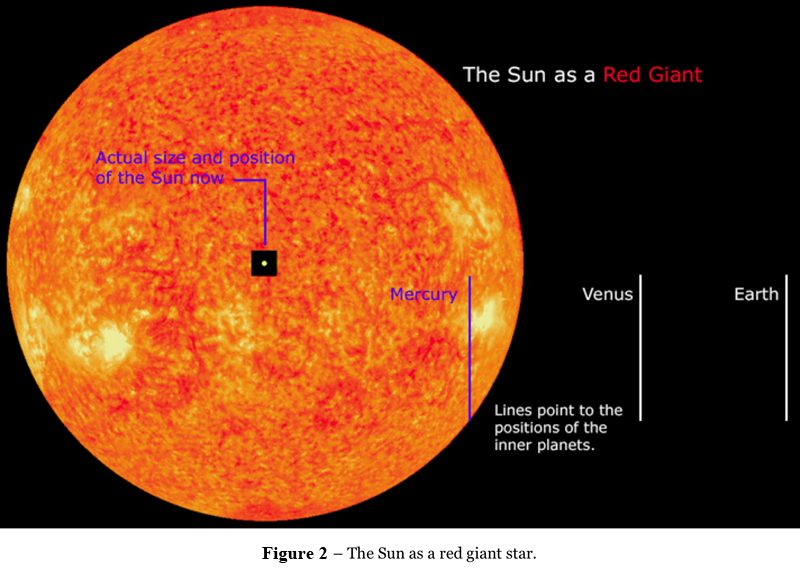
AAlpha Centauri BProcyon B CBarnards Star DPolaris. The Sun The Solar System was formed around 46 billion years ago from a large cloud of dust and gas called a nebula. Red giant star When all the hydrogen has been used up in the fusion process larger nuclei begin to form and the star may expand to become a red giant.
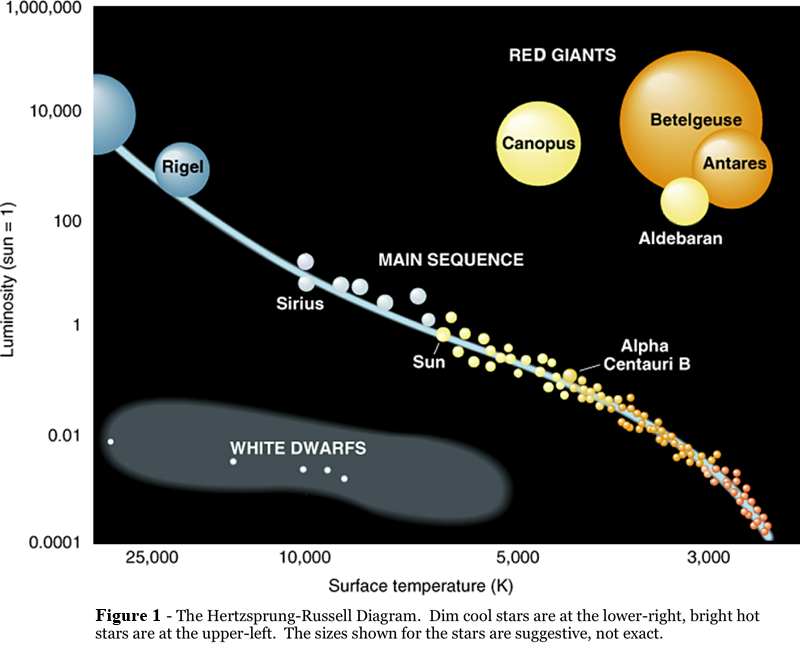
But what is happening here is the description of the changes in the weather as a battle between different elements. Once it is complete you can click on Data Table upper right to see the final values for each stage in the lifecycle. The diagonal dashed line represents the main sequence stars.
This number can be determined from measurements of how bright the sun appears from Earth as well as its distance from us. The compression of its gases raises the density temperature brightness pressure and gravitational force in its. During this process the Sun will lose mass and radiate it away as energy.
The mass of the star Betelgeuse is much greater than the mass of the Sun. Its spin has a tilt of 725 degrees with respect to the plane of the planets orbits. Lifetime energy rate energytime at which sun emits energy The rate at which the sun emits energy its luminosity is around 38 x 10 26 Watts thats the number 38 followed by 25 zeroes - quite a lot of lightbulbs.
The Main Sequence represents a long stable stage of stellar life in which the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium in the core replaces the heat escaping at the surface. Less than the Sun. But there are many ways for our Sun to get a new lease on life and to emit its own powerful radiation once again.
The reason for this is largely due to the second main contributor to the Suns apparent. Describe how small changes in Earths orbit around the sun explain the pattern of glacial and interglacial periods over the past million years. Currently it has more than 72 hydrogen.
The clouds are being chased like a sheepdog chases sheep to return to its rightful position as the top dog in the skies. Since the Sun is not solid different parts rotate at different rates. T he Suns brightness and size will increase with some thermal pulsations as helium burning starts until it is 200 times the size it started.
Depend on the type of star. However this process cannot last forever since there is a finite amount of hydrogen in the core of the Sun. The Sun is at this stable phase in its life.
This collapsed under its own gravity transferring gravitational potential. At the point it loses its outer layers exposing the core of the star and its size drops to about 1100th of its original size as a. We can imagine the sun being the ruler over us.
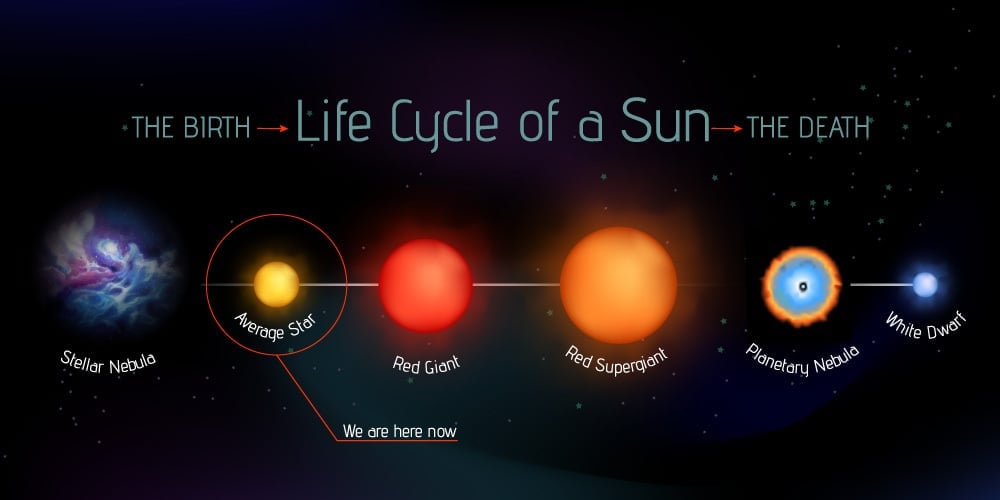
The numbers 1 through 5 represent stages in the life cycle of the Sun. Solar wind is stream of charged. Therefore its total lifetime will be.
Since that point of time Sun has been fusing its Hydrogen fuel into Helium at a steady pace for 45 billion years. Changes in Earths orbit around the sun cause changes in Earths climate that are superimposed on the larger signal driven by greenhouse gases. It Stood Watch over its Realm Looked over You.
This means nuclear fusion reactions in its core fused hydrogen into helium. When the sun was born the percentages were about 94 hydrogen and 4. This shows how the mass of your star varies over its life.
Here Earth is shown to scale with part of the Sun and a giant loop of hot gas erupting from its surface. As the Earth goes around the Sun the Sun appears to go in a cycle from equator to north of equator and then back to equator and then to south of equator and then back again to equator which marks the. Earth and the Sun.
Describe how the Sun changes over its lifetime. It will continue in this state for millions of years to come. Over the next 54 billion years the Sun will continue its life cycle becoming first a red giant then a white dwarf and ultimately when it.
Describe how the Sun changes over its lifetime. The diagram represents the inferred changes to the luminosity and color of the Sun throughout its life cycle. Greater than the Sun.
Because over the last 45 billion years the Sun has been busy converting its Hydrogen into Helium via the Proton-Proton Chain. Compared to when it joins the Main Sequence a stars mass at the end of its life will. At the equator the Sun spins around once about every 25 Earth days but at its poles the Sun rotates once on its axis every 36 Earth days.
Like most stars in our universe the Sun is on the main sequence stage of its life. When earth was first formed its atmosphere was likely composed of hydrogen helium and other gases that contained hydrogen. How does the size of the Sun change over its lifetime.
Prior to reaching the Main Sequence the stars energy source is a gradual contraction.

Pin By Clara Beyer On Inspiration In 2022 Cassiopeia Constellation Astronomy Constellations Constellations

How Has The Composition Of The Earth S Atmosphere Changed Over Time Socratic Earth Atmosphere Atmosphere Earth S Atmosphere

Sun Webquest Astronomy Solar Sun Spots Physical Science Middle School Middle School Physics Teaching Middle School Science

Pin By Nataliya Babiychuk On Poetry How Are You Feeling Feeling Alone Pillow Thoughts

What Is The Life Cycle Of The Sun Universe Today
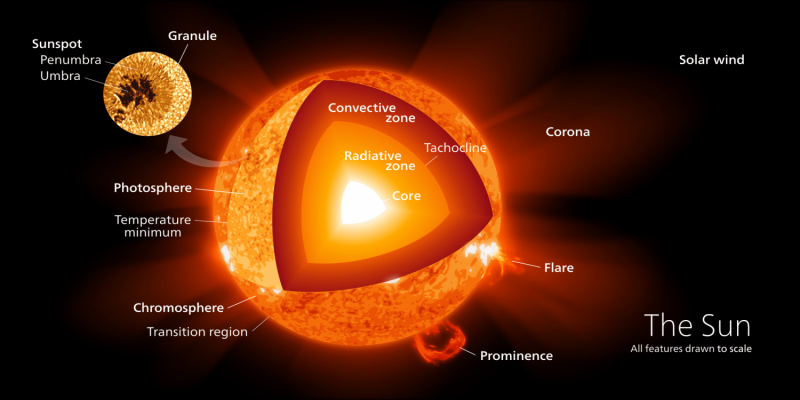
How Does The Sun Produce Energy

Our Solar System Solar System Projects Astronomy Solar System Facts

Tips For Saving Energy At Home Homeenergysaving Save Energy Energy Saving Devices Energy Saving Tips

Our Genome Changes Over Lifetime And May Explain Many Late Onset Diseases Dna Art Dna Logo Science Art

What Is The Life Cycle Of The Sun Universe Today
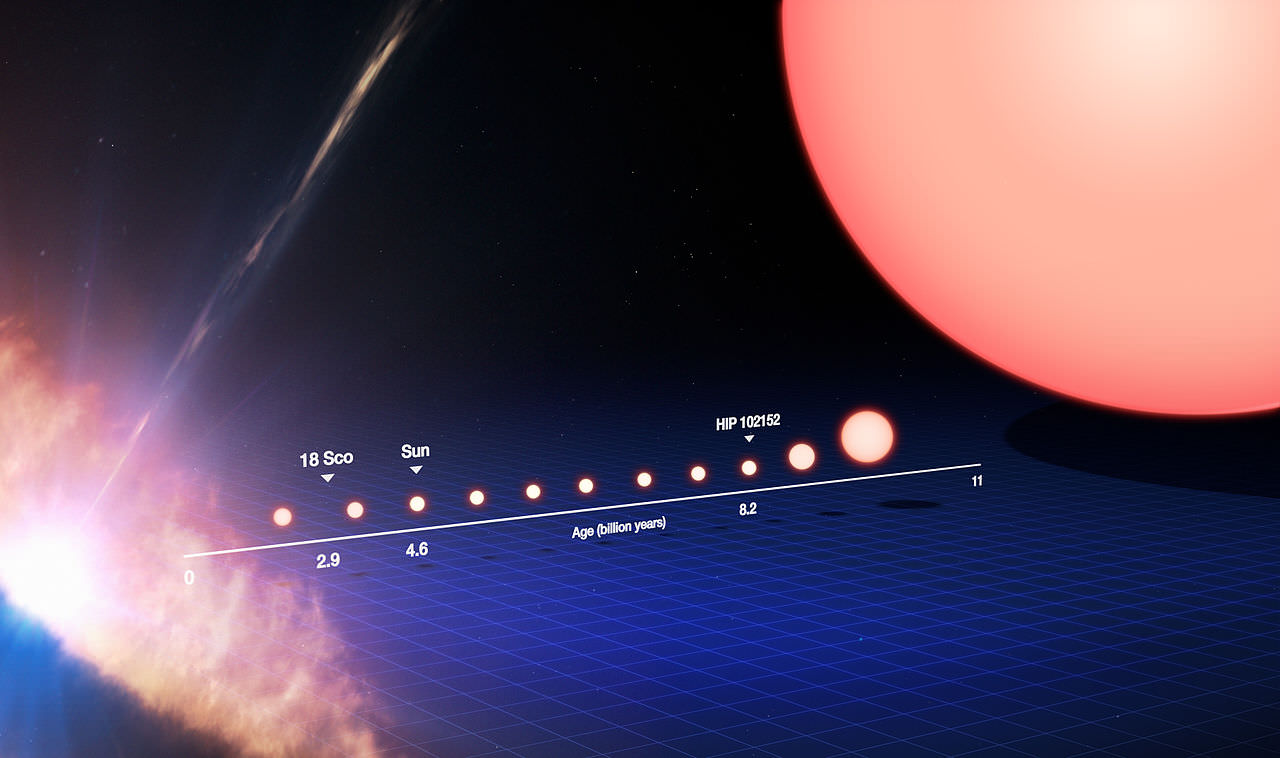
What Is The Life Cycle Of The Sun Universe Today

Winner Of Best Time Lapse At Los Angeles Independent Film Festival Awards Laiffawards Com May Winner Html Lofoten See The Northern Lights Solar Activity

What Is The Life Cycle Of The Sun Universe Today
Age Of The Sun How Old Is The Sun How Much Longer Will The Sun Last

What Is The Life Cycle Of The Sun Universe Today

Sketchplanations A Weekly Explanation In A Sketch Psychology Facts Reading Books To Read

Comments
Post a Comment